As the globe continues to evolve, so do the rate and frequency of our monetary transactions. And in an increasingly digital environment, it is more critical than ever to secure these transactions with diligence.
Today, fraudsters can hide behind the great anonymity of the internet, and the opportunity to conduct fraud has increased in tandem. For this reason, contemporary technology remains an essential issue in discussions about cybersecurity; its role has become both urgent and unavoidable.
What is fraud detection in banking?
Detection of banking fraud is a collection of strategies and procedures meant to decrease risk. Due to their fast access to cash and capacity to move them, financial institutions are among criminals’ most often targeted businesses.
Banks and fintech institutions invest in comprehensive fraud detection and prevention technologies to secure their assets, systems, and clients.
Strictly speaking, fraud detection focuses on recognizing fraudsters’ attempts, whereas fraud prevention focuses on stopping them. However, in practice, both tactics are almost interchangeable, as they work hand in hand.
SEON provides methods for detecting and preventing digital banking fraud that do not create conflict or false positives.
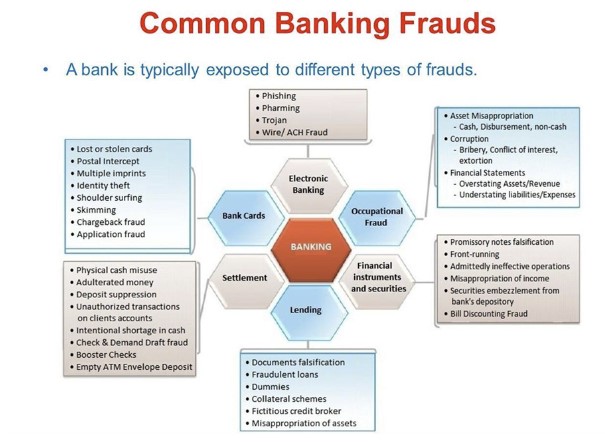
Common kinds of frauds to be aware of
Although few predicted the industry’s development when Moven and Chime debuted in 2007, digital banks have made significant progress. This industry alone is projected to reach $395 billion by 2026.
All because of their efficient onboarding and complaint response procedures.
Unfortunately, fraudsters are aware of all this success and continuously launching assaults to take advantage of these rapid procedures.
Before we try to learn about the technology and tactics that safeguard us, we must comprehend the types of financial fraud we face. While some of these fraud schemes have existed for eons, the digital age has merely augmented these “bad actors'” capabilities. The following are frequent scam schemes to watch out for:
-
Wire Fraud
Wire fraud is a crime that can use several channels of contemporary communication, such as the telephone, fax, email, and even social media. They employ these strategies to convince the bank that they are obtaining large quantities of money from a legitimate source while posing as someone else.
-
Theft of Credentials
In these cases, the thief employs illicit methods to get data that uniquely identifies a person. Using the widespread tactic of “phishing,” the criminal pretends as a reputable firm to deceive the victim into divulging sensitive information. It might be anything from a social security number, an ID number, or even verification responses for resetting a password.
-
Account Takeover
It is commonly known as identity theft, and is a very effective extension of credential theft. With so many firms storing their data on cloud-based systems, it is simpler than ever for a single access point to provide total control. The greater our reliance on internet services, the greater our vulnerability.
-
Money Laundering
Any funds obtained fraudulently or illegally must be “cleaned” or legitimized through money laundering. This procedure involves sending the cash through authorized channels and verifying it from numerous sources. Banks typically accomplish this because they can transfer vast amounts of money from one account to another.
-
Accounting Fraud
Accounting fraud occurs in the business loan industry. With no will of debt repayment, the criminal will ask for a loan using fabricated bank statements using a fictitious firm. Once they have the money, they can vanish while the bank absorbs the loss.
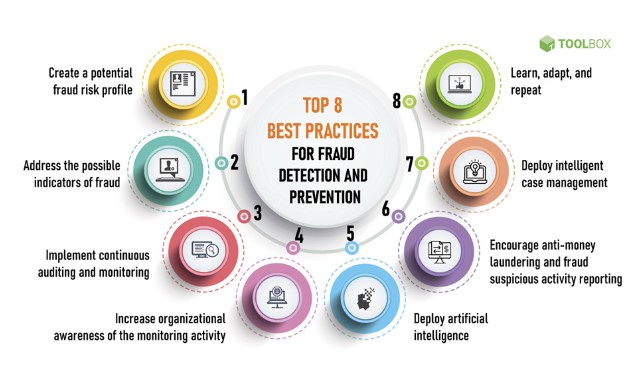
The technology used to combat fraud
As fraud becomes increasingly complex, so do the countermeasures we employ to combat it. SEON’s fraud detection and prevention solutions help keep fraudsters in check, despite their methods becoming more sophisticated. Below are the five most prevalent ways to prevent financial fraud:
1. Artificial Intelligence
It would be practically difficult for a person to personally validate each transaction, given the number of daily transactions that banks are responsible for validating. Many of these transactions are occurring concurrently, resulting in an insurmountable backlog of activities for a single employee, lowering the customer-expectations-driven pace. Banks currently employ AI-based automated systems built to monitor the behavior and identify fraudulent conduct on their behalf.
2. Biometric data
When constructing passwords, we can only use a limited number of distinct characters. The likelihood of passwords being exposed through malicious channels is increasing, and a random assortment of characters and numbers can only get you so far. The cadence of your voice, the symmetry of your face, and other distinctive attributes are utilized to generate biometric information.
This additional degree of security makes it more challenging to forge someone’s identity. It offers an entirely new layer of protection that thieves cannot crack as readily as regular passwords. Real-time data enrichment augments customers’ Know Your Customer (KYC) data with aggregated additional data gathered from various sources, including open-source databases, digital services, and social networks.
SEON is useful for fraud detection since it enables you to make more informed judgments regarding risk.
The data enrichment modules of SEON give an abundance of meaningful data points, beginning with the simple information supplied by clients.
3. Consortium data
When creating fraud detection systems, the more data extracted, the better. If the data comes from various sources, you create complexity for people attempting to connect to your network. When banks collaborate to exchange fraud data and online system risks, the automated system has a far more transparent view of what it is battling.
Typically, a fraud offender has several victims, indicating a pattern among comparable targets. Combining this data doubles the system’s backend security and analysis significantly. Data from a consortium provides the advantage of collective intelligence within the same business, where the information is used to combat fraud.
4. Technical standardization
Generally, a comprehensive perspective of your systems is the most effective method to comprehend precisely what is occurring with your money. The easiest way to get this perspective is to ensure that all of your company’s data resides in the same system and remove as many components of your business as possible from your old legacy system.
Many of these “legacy systems” feature large funnel holes that fraud offenders can exploit, with some systems still relying on physical ledgers and paper records to bridge gaps. You can use Seon, as the quicker you combine your internal systems into a single solution, the easier it will be to recognize suspicious conduct.
5. Machine Learning
Companies are discovering that simple rule-based AI solutions cannot keep up with the complex fraud landscape. With machine learning, you can create a cybersecurity system that modifies its rules based on historical behavior.
Whereas traditional AI still requires some human control, machine learning employs an automated mechanism that regularly removes the time and effort needed to update or alter security parameters. Using deep learning models to discover the nuances of behavioral analysis, you can identify sessions that pose a significant risk yet are lying in plain sight.
6. Governance, Risk, and Compliance (GRC)
The described technology is only as effective as the programs that harness it. Not only does the use of GRC systems secure your data, but it also provides a set of processes that assist organizations in achieving their goals, addressing risk, and acting with integrity. Together, these principles offer comprehensive security and coverage for your data landscape.
Each principle complements the other two, and all three consider the same information, individuals, and technology. For instance, a business may be required to comply with a new compliance rule while simultaneously addressing internal protection (or governance) — and these two pillars protect against the danger of a data infringement.
7. Access Risk Management or ARM
In handling accessibility risks, ARM includes strategies for identifying, evaluating, and prioritizing risks from an access provisioning and compliance standpoint. The ARM methodology enables the diligent monitoring of your data and the implementation of pre-emptive actions to manage access across all users and accounts. Without a well-thought-out solution, it is exceedingly difficult to accurately recognize financial fraud on your network. ARM not only lets you determine when anything is wrong but also provides a clear idea of how, when, and where to respond to a particular breach.
Final Thoughts
Using automated, intelligent technologies to decrease risk and increase security reduces wasted time while increasing protective vigilance. Seon can assist with fraud prevention by safeguarding digital identities.
The objective is to employ scalable, resilient risk technology that provides a seamless client experience. SEON delivers a comprehensive selection of modular APIs from which you may select only the APIs you need to integrate to obtain richer data.