Students and young professionals in the field of finance, especially financial analysis and asset management, often wonder which of the many professional designations they should pursue.
The two most widely recognized designations within investment management are the CFA (Chartered Financial Analyst) designation, and the CAIA (Chartered Alternative Investment Analyst) designation.
This article will provide a high overview of each designation and compare the requirements to earn each designation.
Exam Topic Areas
CFA exam topics include quantitative analysis, general economics, financial reporting and analysis, corporate finance, equity investments, fixed income, and portfolio management.
The CAIA designation focuses on alternative assets, which include hedge funds, venture capital, private equity, commodities, real estate investments, and structured products.
Alternative Assets
Alternative assets are covered to some extent in the CFA exam, but the CAIA goes deeper into the subject.
Specific topics for the CAIA exam include real estate, commodities, hedge funds, private equity, structured products, and risk management.
Analysis of alternative investments is significantly different from traditional investments like stocks and bonds.
Evaluating Options
Pursuing the CFA designation makes sense regardless of whether you plan to work in traditional investment fields or within more specialty alternative asset segments.
If you plan to work for alternative asset managers like Blackstone, Macquarie, LaSalle, private equity firms and hedge funds like Bridgewater Associates, the Carlyle Group, etc., then a designation like the CAIA could be a great supplement in addition to the CFA designation.
Let’s look at exam requirements in more detail.
Exam Requirements
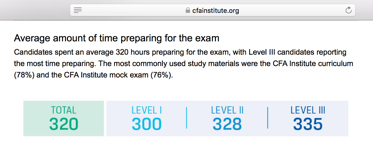
Passing either exam requires significant studying. The CFA Institute recommends about 300 hours of study for each of the three levels (see insert below). Many students who have successfully passed the exam, report spending up to twice that much time per exam.
The CAIA exam, administered by the CAIA Association, recommends about 200 study hours for each of its two exam levels.
Both exams require registration fees. The CAIA costs approx. $2,900 and the CFA exam requires approx. $2,350 for each exam.
In order to take the CFA exam, an applicant must hold a Bachelor’s degree from an accredited university or be in the final year of the program.
Once a candidate has passed the level 3 exam, they have to wait until earning at least four full years of relevant work experience before their charter will be issued.
After passing all three exams and meeting the required work experience, a CFA candidate will be able to use the CFA designation.
Test Your Skills with Free Practice Questions
Click below for a free trial of Wiley’s CFA pre course:
CAIA Requirements
There are no prerequisites for taking the CAIA tests, but having passed, you are expected to have four years of relevant experience or one year of work experience and a Bachelor’s degree in order to claim the CAIA title.
Exam Difficulty
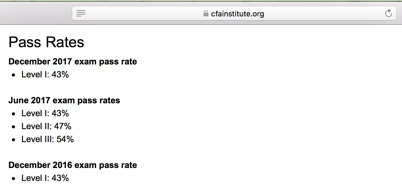
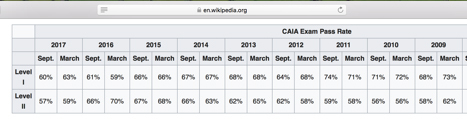
The CFA exam is harder according to both student surveys and official pass rates.
Only 43% of CFA test takers pass Level 1, with 47% passing Level 2 and 54% passing Level 3, whereas for CAIA, pass rates are higher for both Level 1 (63% in 2017) and Level 2 (59%).
Exam Availability
CFA exam levels 2 and 3 are held once a year in June. Level I of the CFA exam given twice a year, in December and June.
Both levels of the CAIA exam are held twice a year.
You could theoretically try to take these exams simultaneously, but in practice, I would advise against it.
CFA or CAIA
The CFA exam is such a rigorous course of study that I would avoid any additional obligations if I could help it.
On the other side, if you plan to take both exams, absolutely do, but take CFA exam first. The CAIA exam will seem much easier after you have taken the CFA exam.
The CFA exam books are excellent, very detailed and comprehensive, but you need to start studying very early in order to give yourself enough time to wade through all the text.
You may also want to consider one of the best CFA exam review courses available to help you study for the exam. Regularly practicing CFA exam test questions from one of the test banks is a great way to retain the material.
CAIA Books
The CAIA textbooks cover less material and don’t require as much time to read. The textbooks have a somewhat less convenient format, with fewer examples, fewer blocks within a chapter, and fewer practice problems compared with the CFA textbooks.
There are also a variety of prep courses available for CAIA as well.
Membership Costs
Another note about having both designations is the membership fees. Once the designations are awarded, the annual membership fee for the CFA charter is $275.
Maintaining the CAIA requires $350 (with a two-year option for $650).
The fees required for maintaining both designations along with a brokerage or insurance license can quickly up. But if you are working full time, many firms will reimburse your membership costs.
Career Prospects
Every analytical position in finance can benefit from the CFA designation, both by being more competitive in the marketplace, and by gaining extensive skills and knowledge necessary to do an excellent job.
Certain occupations, especially in asset management, require every portfolio manager and fund manager to have the CFA charter. In return, the average salaries for CFA charterholders can be very high.
Specialists with the CAIA designation are most frequently employed by asset managers like Blackrock, HSBC, Credit Suisse, Deutsche Bank, JP Morgan etc., as well as private equity firms and a hedge funds, which due to their boutique size may have more limited positions.
Additional Career Options
If you plan to work with individual investors, many people also evaluate the CFA vs CFP. Sometimes financial advisors also benefit from considering the CFA vs CPA due to the more specialized estate planning considerations.
Final Thoughts
Whether you are going to be working with traditional or alternative assets, both designations offer valuable career benefits ranging from marketability to the potential for increased salaries.
The CFA designation offers a broad and versatile skillset that can be applicable for most investment management roles.
The CAIA offers a more specialized program that is more applicable to positions within the alternative asset management space. Professionals in these positions frequently hold both the CFA charter and the CAIA designation.